What are the 4 types of agents in AI is a crucial question when exploring artificial intelligence’s impact on our rapidly evolving technological world. Answering it opens the door to comprehending how machines ‘think’, act, and fundamentally shape the future, providing vital clarity on their diverse functions and the mechanisms driving intelligent behavior in AI systems, a topic this article will thoroughly explore.
Contents
What is an AI agent?
Before delving into specific types, we need to define an “AI agent.” An AI agent is any entity capable of perceiving its environment through sensors and acting upon that environment through actuators. The goal of an AI agent is to perform actions to achieve specific goals or optimize a performance measure. Understanding this basic definition is foundational before we tackle what are the 4 types of agents in ai.
For example, an autonomous vacuum cleaner robot is an AI agent. Its sensors might include cameras, bump sensors, and dust sensors. Its actuators are its wheels and suction motor. Its goal is to clean the floor.
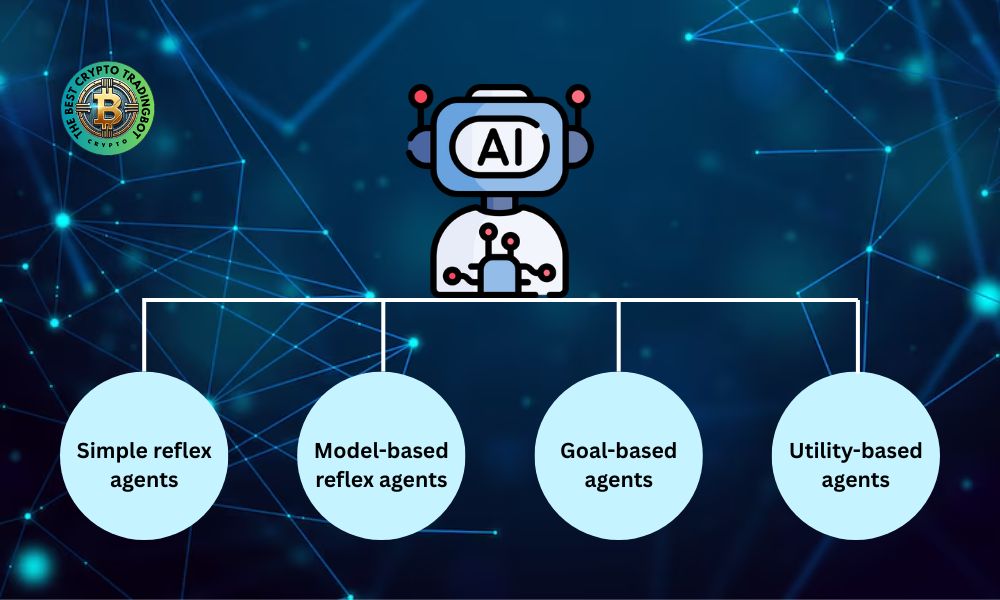
Now, let’s explore the 4 basic types of AI agents, which form the core answer to what are the 4 types of agents in ai
Simple reflex agents
These are the most basic type of AI agents. They operate on the “condition-action rule.” This means they only react to what they perceive in the current moment (current percept) without considering the history of previous percepts. This is the first, most fundamental category when considering what are the 4 types of agents in ai.
How they work:
- Sensors gather information about the current state of the environment.
- This information is matched against a set of predefined condition-action rules.
- If a condition is met, the corresponding action is executed via the actuators.
Examples:
- A simple thermostat: if room temperature < set point, turn on heater; if room temperature > set point, turn off heater.
- An autonomous vacuum cleaner changing direction when it encounters an obstacle.
Advantages: Simple, easy to implement, fast reaction time.
Disadvantages: Very limited. They cannot operate effectively in complex environments or when the current state does not provide enough information to make the right decision. They can also easily get stuck in infinite loops if the environment changes unexpectedly.
Model-based reflex agents
To overcome the limitations of simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents were developed. This type of agent maintains an internal “model” of how the world works. This model helps the agent keep track of the state of parts of the environment it cannot currently observe directly. These agents represent a step up in complexity within the framework of what are the 4 types of agents in ai.
How they work:
- Similar to simple reflex agents, they receive information from sensors.
- However, they use an internal model to update their understanding of the current state of the world. This model is built based on the history of percepts and knowledge of how actions affect the environment.
- Based on the state inferred from the model, the agent chooses an action through condition-action rules.
Examples:
A self-driving car needs to know the location of other cars even if they are temporarily obscured. It uses a model to predict their positions based on previous speed and direction.
A robot navigating a maze, remembering paths already tried.
Advantages: Better at handling partially observable environments.
Disadvantages: Building and maintaining an accurate model of the world can be very complex.
Goal-based agents
Goal-based agents are capable of more complex decision-making. Instead of just reacting to the environment, they have information about a “goal” they need to achieve. They choose actions to move closer to that goal. Their ability to plan makes them a significant component in understanding what are the 4 types of agents in ai.
How they work:
- In addition to a model of the world, this agent has information about its desired goal.
- It uses search and planning algorithms to find a sequence of actions that can lead to achieving the goal.
- This may involve considering the long-term consequences of actions.
Examples:
A GPS navigation system finding the shortest or fastest route to a destination.
A robot in a factory needing to move an object from location A to location B. It will plan the steps of moving, picking up, and placing to complete the task.
Advantages: Much more flexible than reflex agents. They can adapt to different situations to achieve their goals.
Disadvantages: The search and planning process can be time-consuming and computationally expensive, especially in complex environments with many possibilities.
Utility-based agents
When there are multiple ways to achieve a goal, or when goals might conflict, goal-based agents may not be sufficient. Utility-based agents will choose the action that yields the highest “utility,” or in other words, the highest level of “happiness” or “satisfaction.” This sophisticated decision-making process is key to appreciating the full spectrum of what are the 4 types of agents in ai.
How they work:
- This agent has a utility function to evaluate the desirability of different world states.
- When faced with multiple action choices, it will estimate the expected utility of the resulting states for each action.
- It chooses the action that leads to the state with the highest expected utility.
- This is particularly useful when there is uncertainty about the outcome of actions or when there are multiple conflicting goals to balance.
Examples:
- A product recommendation system trying to maximize the likelihood of a user making a purchase and their satisfaction.
- An automated trading robot in the stock market, trying to maximize profit while managing risk.
Advantages: Provides a rational approach to decision-making in complex, uncertain, or multi-objective situations.
Disadvantages: Defining and quantifying a suitable utility function can be very difficult and subjective.
Learning agents
An important supplementary concept is that any of these agent types can be enhanced with a “learning element.” Learning agents can improve their performance over time through experience. They can self-adjust rules, models, or utility functions. This learning capability can be applied to enhance any of the previously discussed solutions when we ask what are the 4 types of agents in ai.
In essence, understanding what are the 4 types of agents in AI – simple reflex, model-based, goal-based, and utility-based – is key to grasping AI’s diverse capabilities. To continue your journey into AI and stay updated on tech breakthroughs, make sure to follow The Best Crypto TradingBot for more insightful content!
