What is agent in artificial intelligence is a foundational question for anyone entering the AI field. Essentially, an agent is any entity capable of perceiving its environment through sensors and acting upon that environment through actuators to achieve a specific goal. This simple but powerful concept forms the basis for most modern intelligent systems we interact with daily.
Contents
What is agent in artificial intelligence?
In the vast domain of artificial intelligence (AI), the concept of an “agent” stands as one of the most fundamental and crucial building blocks. An agent is not necessarily a humanoid robot from science fiction films. It can be a software program, a physical system, or even an organization.
To define it simply: An agent is an autonomous entity that observes its environment through sensors and acts within that environment using actuators.
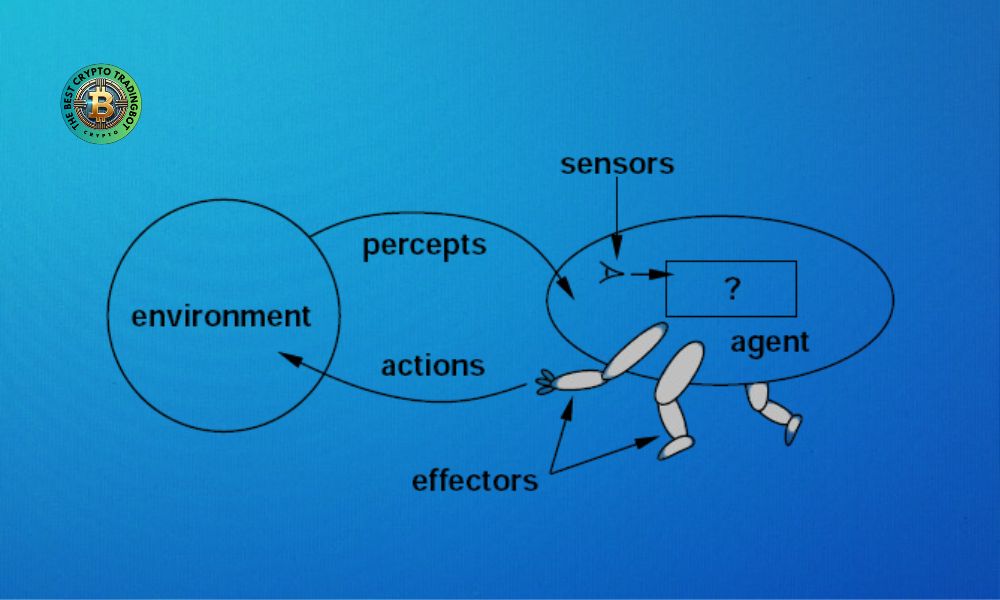
To visualize this, consider a human as a biological agent:
- Environment: The physical world.
- Sensors: Eyes, ears, nose, skin (perceiving sights, sounds, smells, and textures).
- Actuators: Hands, legs, mouth (for moving, manipulating objects, and speaking).
The goal of an agent is to act rationally to achieve the best possible outcome. Therefore, the core of our quest for understanding what is an agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems is to learn how we build automated systems capable of making intelligent decisions.
Core components of an agent: The PEAS model
To design and evaluate an agent, AI researchers often use the PEAS framework. This acronym represents the four core components that define an agent’s task environment:
- P – Performance measure: The criteria for evaluating the agent’s success. For an autonomous vacuum cleaner, this could be the amount of dirt cleaned, the time taken, and the energy consumed.
- E – Environment: The space where the agent operates. This can be physical (a room, a road) or virtual (a website, a chessboard).
- A – Actuators: The parts the agent uses to perform actions. For the vacuum robot, these are the wheels, suction motor, and brushes.
- S – Sensors: The parts the agent uses to perceive the environment. The vacuum might have cameras, infrared sensors for obstacle detection, and dirt sensors.
A key framework for understanding what is agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems is applying this PEAS model. For instance, a self-driving car would have:
- Performance measure: Safety, speed, adherence to traffic laws, passenger comfort.
- Environment: Roads, highways, other vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signals.
- Actuators: Steering wheel, accelerator, brake, signal lights.
- Sensors: Cameras, radar, lidar, GPS, odometers.
Classifying the types of agents in artificial intelligence
Agents are categorized into several types based on their intelligence and complexity. The next step in understanding what is agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems is to differentiate between them.
Simple reflex agents
These are the most basic agents. They act only based on the current percept, ignoring the rest of the percept history. Their logic is based on simple “condition-action” (if-then) rules.
Example: An automated thermostat. If its sensor detects the room temperature is above the set point, it turns on the air conditioning.
Model-based reflex agents
This type is slightly more complex. They maintain an internal “model” or “state” of the world. This model helps the agent track aspects of the environment that cannot be directly observed at the current moment. This internal state is a crucial concept for understanding what is agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems.
Example: A self-driving car needs to remember the location of other cars even when they enter a camera’s blind spot.
Goal-based agents
As we delve deeper into understanding what is agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems, we encounter more sophisticated agents. These agents not only act based on the current state but also have information about a specific “goal.” They choose actions that will lead them toward achieving that goal, which requires deliberation and planning.
Example: A GPS navigation system. The goal is to get from point A to point B. The agent considers various routes to find the optimal path.
Utility-based agents
This is an advanced form of a goal-based agent. Sometimes there are multiple ways to reach a goal, but some are “better” than others. A utility-based agent chooses the action that maximizes its “utility” (degree of happiness or satisfaction).
Example: A GPS not only finds a route to the destination (goal) but finds the fastest route, the one with the lowest fuel consumption, or the one that avoids traffic jams (utility).
Learning agents
The pinnacle of understanding what is agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems lies in learning agents. These are the most complex and intelligent agents, capable of improving their performance through experience. A learning agent has a “learning element” that allows it to modify its knowledge and behavior over time.
Example: A chess-playing program that learns from past games to make better moves, or recommendation systems on e-commerce sites.
Real-world applications of agents

Our exploration of understanding what is agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems would be incomplete without looking at real-world applications. The agent concept is the foundation for countless AI applications in our lives:
Virtual assistants: Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa are software agents.
Robotics: Industrial robots, vacuum cleaners, and autonomous drones.
Recommendation systems: Netflix suggesting movies, Amazon recommending products. Each of these examples is a practical demonstration that helps in understanding what is agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems.
Video games: Non-player characters (NPCs) that act as agents within the game world.
Finance: Automated trading bots that operate on the stock market.
In conclusion, understanding what is agent in artificial intelligence and exploring the different types of agents in modern ai systems is fundamental to grasping AI’s potential. They are the core autonomous entities that turn artificial intelligence from theory into practical application. For more exciting insights into AI and technology, be sure to follow The Best Crypto Trading Bot.
